Claims
‘Low Fat’, ‘High Fibre’, ‘Source of Calcium’, ‘Biotin contributes to the maintenance of normal skin’, ‘Superfood’– are you confused and what do they mean?
Incorrect declaration of Nutrition and/or Health Claims are one of the top reasons for withdrawals of products from sale and legislation around the claims is complex and easy to misinterpret. All nutrition and health claims must be authorised for use on the Nutrition and Health Claims Register (NHCR), and the conditions for use should be fulfilled.
Food Labelling Services can check any Health or Nutrition claim and ensure that it is compliant with the requirements of EC 1924/2006 and the Nutrition and Health Claims Register. The Nutrition and Health Claims Regulation (EC/1924/2006) was introduced with the aim of improving consumer protection by preventing unsubstantiated, exaggerated, or untruthful claims about foodstuffs. It aims to ensure that claims made about food are substantiated by scientific evidence, are not misleadingly worded, and are consistent across the EU.

HEALTH CLAIMS are complex. A health claim is any claim that states, suggests, or implies that a relationship exists between a food category, a food or one of its components and health. Authorised health claims are significantly different and require different rules to general health claims – all need an expert’s advice to ensure that they are compliant.
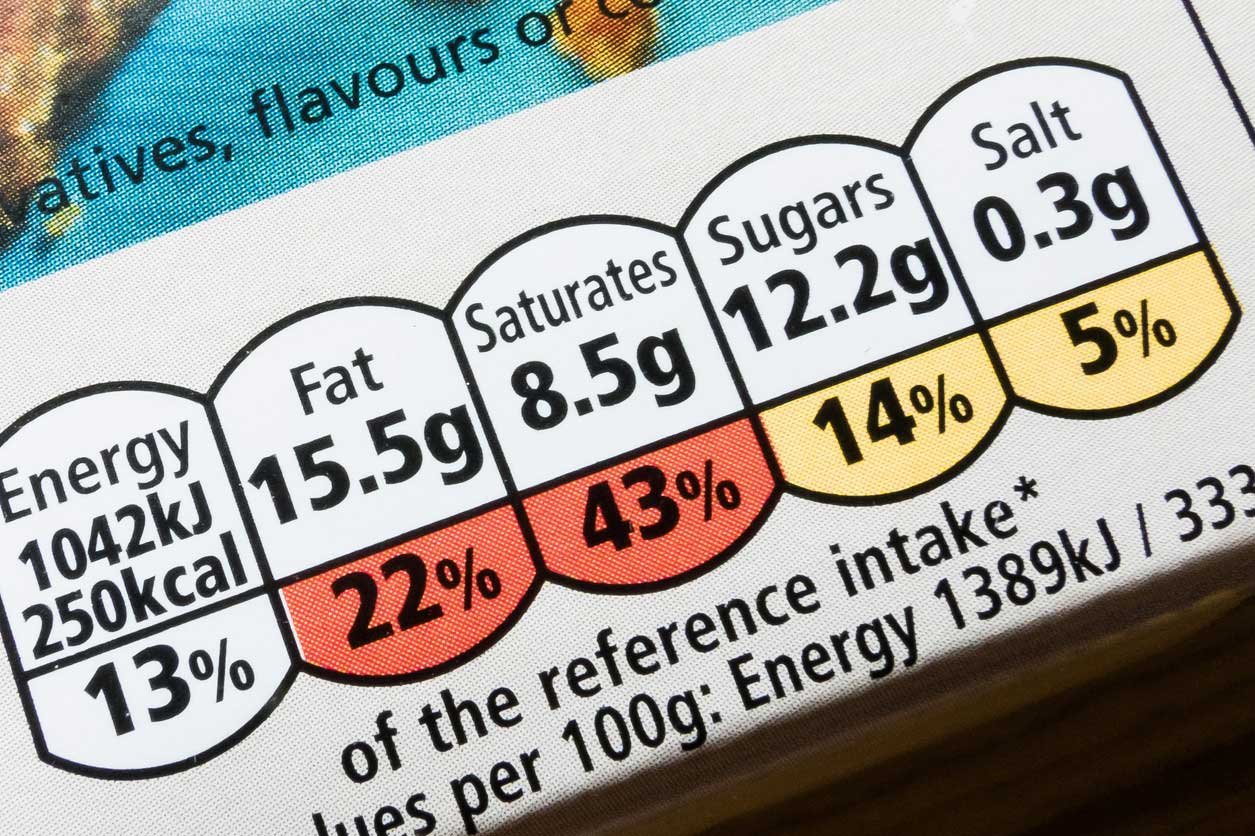
NUTRITION CLAIMS are those which state, suggest or imply that a food has particular beneficial nutritional properties. Comparative nutrition claims are permitted but the circumstances under which they can be made are heavily restricted – again an expert's advice is recommended.
ENVIRONMENTAL CLAIMS should be clear and fully substantiated. If unqualified, claims could mislead the consumer if they omit significant information. All stages of the life cycles of the product should be considered, from the production of the agricultural inputs, through agriculture, production of non-agricultural ingredients, transport, processing, packaging, storage, distribution both at the manufacture and retail level until the product reaches the retail shelf.
